1.Cladograms can be created by comparing DNA or protein sequences. The cladogram on the left is based on DNA sequences and the cladogram on the right is based on comparing protein sequences.
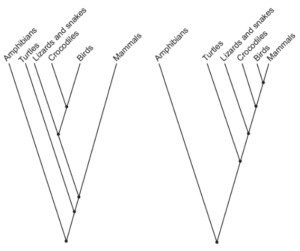
What is the reason that cladograms based on DNA sequences are more reliable predictors of the phylogenetic relationship of species than cladograms based on protein sequences?