26.

Male flies, heterozygous for both grey body and normal wings, were mated with black-bodied, vestigial-winged females. 2000 offspring were counted. The resulting percentage of each type of offspring is shown in the table below.
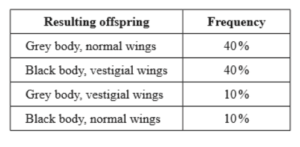
What conclusion can be drawn from the information given above?