4. A DNA profile was made of one individual in a paternity suit. Locus B was used to distinguish between this individual and other individuals. The individual had two alleles of the gene at locus B which are shown below:
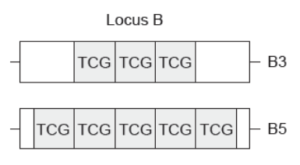
Gel electrophoresis was used to separate and visualize the alleles B3 and B5. The gel, with two bands of DNA, is shown below.
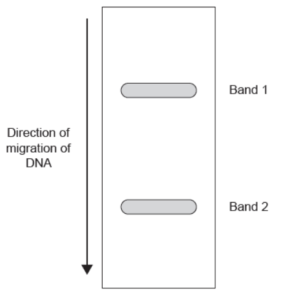
What DNA is in bands 1 and 2?
