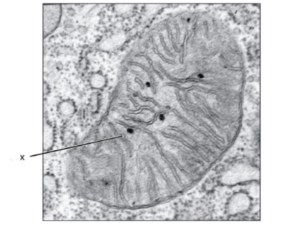
17. What is the structure labeled X in the electron micrograph of a rat liver cell?
[Source: “0315 Mitochondrion new” by OpenStax College - Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Web site.
http://cnx.org/content/col11496/1.6/, Jun 19, 2013.. Licensed under CC BY 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons -
https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:0315_Mitochondrion_new.jpg#/media/File:0315_Mitochondrion_new.jpg]